
For triangle ABC, where AM is the median from vertex.
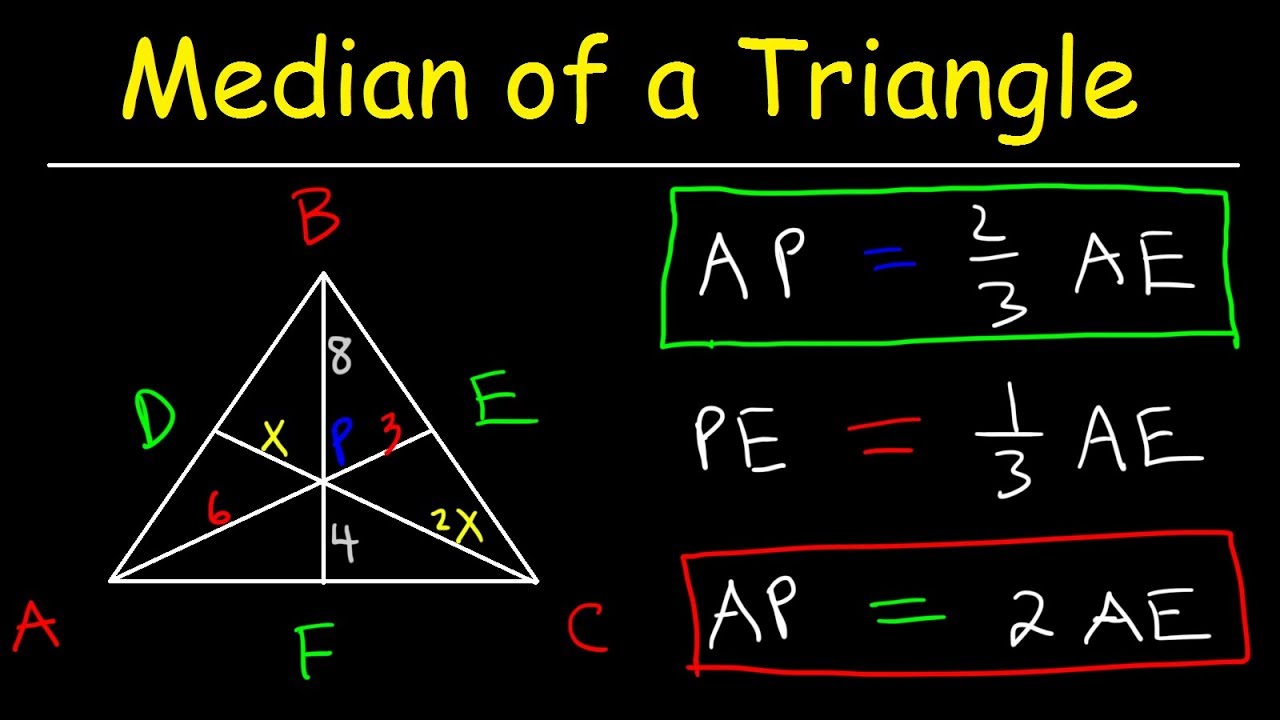
In a triangle, a median is a line joining a vertex with the mid-point of the opposite side. ProofĬonsider a triangle ABC Let D be the midpoint of, E be the midpoint of, F be the midpoint of, and O be the centroid.īy definition. Thus and, where represents the area of triangle these hold because in each case the two triangles have bases of equal length and share a common altitude from the (extended) base, and a triangle's area equals one-half its base times its height. Using the same method, you can show that. The lengths of the medians can be obtained from Apollonius' theorem as: He has a masters degree in writing and literature. The median of a triangle can be constructed by drawing a line segment from the vertex of the triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side.
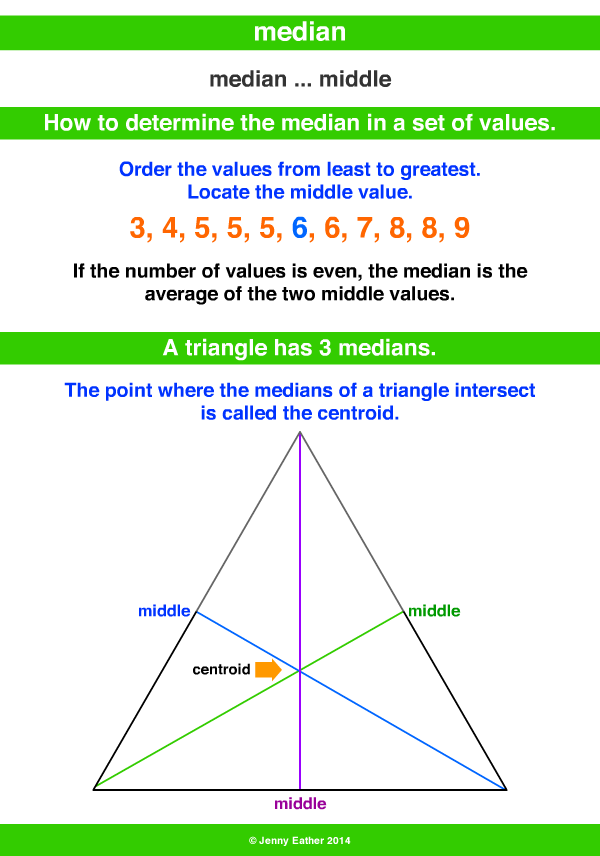
In normal median, we find a point that has minimum sum of distances. Thus we have the relationships: Other properties Where a, b and c are the sides of the triangle with respective medians m a, m b, and m c from their midpoints. The centroid divides each median into parts in the ratio 2:1, with the centroid being twice as close to the midpoint of a side as it is to the opposite vertex.įor any triangle, (perimeter) < sum of the medians < (perimeter).What is the Median and Altitude of a TriangleĪ closed figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle. It is a 3-sided polygon and is named as ‘ΔABC’. (a) Number of sides forming ΔABC are 3, i.e., AB, BC, and CA. (b) Number of vertices (i.e., initial and terminal points of sides) are 3, i.e., A, B, and C. (c) Number of angles are 3, i.e., ∠A, ∠B, and ∠C. (d) Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°, i.e., ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°. The side AB is called the base line of ΔABC and the angle formed at vertex C opposite the base line AB is called the vertical angle. Interior and exterior of a triangleĪ triangle drawn on a plane divides the plane into 3 parts interior, exterior, and the triangle itself. The points lying inside ΔABC (i.e., cross) forms the interior of ΔABC and the points lying outside ΔABC (i.e., dots) forms the exterior of the ΔABC. Linear boundary of the triangle is the triangle itself. Altitude of a triangleĪn altitude of a triangle is the line segment drawn from a vertex of a triangle, perpendicular to the line containing the opposite side. The three medians meet at one point called centroid - point G. (i) PS is an altitude on side QR in figure. (ii) AD is an altitude, with D the foot of perpendicular lying on BC in figure. (iii) The side PQ, itself is an altitude to base QR of right angled PQR in figure. (ii) All the three altitudes meet at a point H (called orthocentre of triangle) i.e., all altitudes of any triangle are concurrent. (iii) Orthocentre of the triangle may lie inside the triangle, outside the triangle and on the triangle.

Although altitude of a triangle is a line segment, but in the statement of their concurrence property, the term altitude means a line containing the altitude (line segment).ġ.Since the altitudes of a triangle are concurrent, therefore to locate the orthocentre of a triangle, it is sufficient to draw its two altitudes.The point of concurrence of the altitudes of a triangle is called the orthocentre of the triangle. The altitudes of an equilateral triangle are equal.ġ. The orthocentre of an acute-angled triangle lies in the interior of the triangle.Ģ. The altitude bisects the base of an equilateral triangle.Ģ. The orthocentre of a right-angled triangle is the vertex containing the right angle.ģ. The altitudes drawn on equal sides of an isosceles triangle are equal.ģ. The orthocentre of an obtuse-angled triangle lies in the exterior of the triangle.Ī line segment that joins a vertex of a triangle to the mid-point of the opposite side is called a median of the triangle.įor example, consider DLMN. Let S be the mid-point of MN, then LS is the line segment joining vertex L to the mid point of its opposite side. The line segment LS is said to be the median of DLMN. Similarly, RN and MT are also medians of DLMN. (ii) All the three medians meet at one point G (called centroid of the triangle) i.e., all medians of any triangle are concurrent.
(iii) The centroid of the triangle always lies inside of triangle. (iv) The centroid of a triangle divides each one of the medians in the ratio 2 : 1. (v) The medians of an equilateral triangle are equal in length.Įxample: The angles of a triangle ABC are in the ratio of 1 : 2 : 3.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
